





| Central Limit Theory |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| q | In the limit, as the sample size becomes large, the sum (or the
mean) of |
|||||||
| a set of independent measurements will have a normal distribution, |
||||||||
| irrespective of the distribution of the raw data. |
||||||||
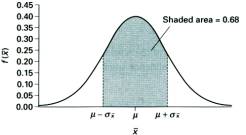
| q | If there is a population which has a mean of mand a standard deviation |
|||||||
| of s, then the distribution of its
sampling means will have: |
||||||||
| (1) | a mean m x = m,
and |
|||||||
| (2) | a standard
deviation sx = s/(N)1/2 = standard error of the mean |
|||||||