





| F-Test |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
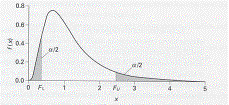
| q | F-distribution is non-symmetric. |
||||||||
| q | There are two critical F values of unequal magnitude. |
||||||||
| q | Whether to use the upper or the lower critical value depends on the |
||||||||
| relative magnitudes of S1 and
S2: |
|||||||||
| If S1
> S2, then use the upper limit
FU to reject the null hypothesis |
|||||||||
| If S1
< S2, then use the
lower limit FL to reject the null
hypothesis |
|||||||||
| q | Or you can always make S1
> S2 when F is defined. In this
case, you |
||||||||
| can always use the upper limit to examine the hypothesis. |
|||||||||